Electric Current
Electric Current: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Electric Current, Potential Difference, Electric Current Density, Charge Flown when Current Is Constant, Charge Flown when Current Is Variable & Calculation of Charge Flown from Current-Time Graph etc.
Important Questions on Electric Current
Current density in a cylindrical wire of radius varies with radial distance as . The current through the section of the wire shown in the figure is.
In hydrogen discharge tube, it is observed that through a given cross-section electrons are moving from right to left and protons are moving from left to right per second. The current(in ) in the discharge tube will be
Current flowing through a wire depends on time as The charge flowing through the cross-section of the wire in time to is
The amount of charge passed in time through a cross section of a wire is The value of current at time is
Current is flowing with a current density in a copper wire. Assuming that each copper atom contributes one free electron and given that
Avogadro number
Density of copper
Atomic weight of copper
The drift velocity of electrons is
A current of is established in a circuit containing an aluminium resistor of length . If the area of cross-section of the resistor is at a point P.The current density at that point will be :
A cylindrical conductor has length and area of cross-section Its conductivity changes with distance from one of its ends as [ is a constant]. The electric field inside the conductor as a function of is when a cell of emf is connected across the ends. Find . [Given that Volt.]
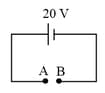
In the shown circuit, what is the potential difference across and ?
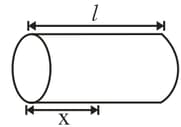
A steady current is set up in a wire whose cross-sectional area decreases in the direction of the flow of the current. Then, as we examine the narrowing region
Number of electrons passes through a wire in minutes is , if current passing through the wire is . Find the value of .
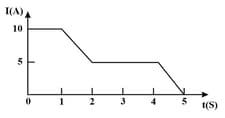
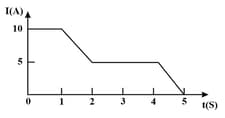
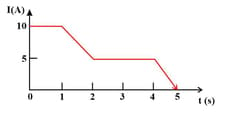
The current through an element is shown in the figure. Determine the total charge that passes through the element after in Coulombs.
In the circuit element given here, if the potential at point then the potentials of and are given as,

The current through an element is shown in the figure. Determine the total charge that passes through the element after in Coulombs.
The current through an element is shown in the figure. Determine the total charge that has passed through the element at in Coulombs.
Number of electrons passes through a wire in minutes is , if current passing through the wire is . Find the value of .
A fully discharged battery (emf, capacity) is connected with a charging device that can supply the battery a steady current, . The battery is connected to charging device for . Final charging level of battery (in percentage) is,
For a cell, the terminal potential difference is when circuit is open and reduces to when cell is connected to a resistance . The internal resistance of the cell is
An electric heater is connected to the voltage supply. Which of the following statment is true about the initial current ,if after few seconds a steady value of current is achived?
Out of the following options, identify the correct direction of flow of current through an electric circuit.
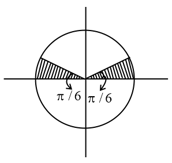
The current and its direction as a result of the flow of electrons from point to point in one microsecond will be